Children's Dentistry
Preventing Problems Before They Start
The health of your child’s teeth and mouth is very important to the well-being of his or her entire body, and while routine brushing and flossing at home is necessary to keep your child’s smile looking its best, visiting the dentist for a comprehensive exam and cleaning is essential. The American Dental Association recommends that your child visit the dentist every six months to ensure his or her teeth stay healthy and smile stays beautiful.
By routinely seeing the dentist for exams and cleanings, your child can:
- Prevent tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath
- Avoid costly and extensive dental procedures
- Have white teeth by reducing staining from food and drinks
- Shorten the time spent in the dentist’s office
- Have a smile that will last a lifetime
The Exam
During your child’s exam, the dentist will thoroughly examine your child’s teeth and gums for signs of tooth decay, gum disease, and other health problems. The dentist may also want to take X-rays to see what is happening beneath the surface of the teeth and gums. Whether these X-rays are traditional or digital, the images provided will help the dentist discover dental issues not visible to the naked eye.
Professional Cleanings
The dental hygienist will begin your child’s cleaning by exploring the surface of the teeth to determine if there are any cavities and to examine the quality of existing fillings. The dental hygienist will then perform a periodontal exam to make sure your child’s gums adhere tightly to the teeth, and no periodontal disease or bone loss is present.
Next, the hygienist will carefully clean your child’s teeth with a variety of tools to remove any hard mineral buildup (tartar) from the teeth. Then, the hygienist will floss your child’s teeth, use a polishing compound, and apply fluoride. Cleanings usually aren’t painful, but if your child has any anxiety about the dental exam, be sure to let the hygienist know. They may offer several sedation options to ensure your child’s comfort. If the dentist or hygienist finds tooth decay or gum disease, they will talk to you about changing your child’s brushing or flossing habits. In severe cases, they may recommend antibiotics or other dental treatments. If your child’s teeth and gums appear to be healthy, the dentist will probably recommend that your child continue his or her brushing and flossing routine as usual.
Fluoride
Your child brushes twice a day, flosses regularly, and visits the dentist every six months. But did you know that rinsing with fluoride – a mineral that helps prevent cavities and tooth decay – also helps keep teeth healthy and strong?
Fluoride is effective in preventing cavities and tooth decay by coating teeth and preventing plaque from building up and hardening on the tooth’s surface.
Fluoride comes in two varieties, systemic and topical:
- Systemic fluoride is ingested, usually through a public water supply. While teeth are forming under the gums, the fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it stronger and more resistant to cavities.
- Fluoride can also be applied topically to help prevent caries (cavities) on teeth present in the mouth. It is delivered through toothpaste, mouthwash, and professional fluoride applications. Professional application of topical fluoride foam and varnishes is also a valuable tool in cavity prevention.
Receiving a fluoride treatment from your dentist
A fluoride treatment in the dentist’s office takes just a few minutes. After the treatment, patients may be asked to not rinse, eat, or drink for at least 30 minutes in order to allow the teeth to absorb the fluoride. Depending on your child’s oral health or your doctor’s recommendation, your child may be required to have a fluoride treatment every three, six, or 12 months. Your doctor may also prescribe at-home fluoride products such as mouthwash, gels, or antibacterial rinses.
How to choose the right fluoride treatment
When choosing an at-home fluoride product (such as toothpaste or mouthwash), always check for the American Dental Association’s (ADA) seal of acceptance. Products marked with the ADA seal of approval have been carefully examined and approved by the ADA based on safety and effectiveness.
Tongue-Tie
Tongue-tie is a birth defect that occurs when the strip of skin (lingual frenulum) connecting a baby’s tongue to the floor of their mouth is shorter than usual. Typically, this strip of skin separates before birth, allowing the tongue free range of motion. With tongue-tie, the lingual frenulum remains attached to the bottom of the tongue.
Tongue-tie is a very common condition that, if addressed quickly, will not hinder a child’s development. However, if left untreated, tongue-tie can result in malnourishment, speech difficulty, or poor oral hygiene.
Signs of tongue-tie include:
- Restriction of the tongue’s movement, making it harder to breastfeed
- Difficulty lifting the tongue up or moving it from side to side
- Difficulty sticking the tongue out
- The tongue looks notched or heart-shaped when stuck out
Treatment of Tongue-Tie
The treatment of tongue-tie for infants is a simple surgical procedure called a frenotomy. Your child’s doctor examines the lingual frenulum and then uses sterile scissors or laser to snip the frenulum free. Stitches are usually not necessary. Since there are few nerve endings or blood vessels in the lingual frenulum, only a local anesthetic is used.
Frenotomy for tongue-tie in older children and adults is similar to that for infants, although it is usually done under general anesthesia and may involve stitches. Speech therapy may also be necessary.
Pediatric Sealants
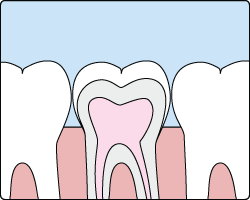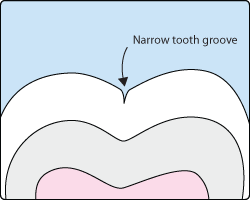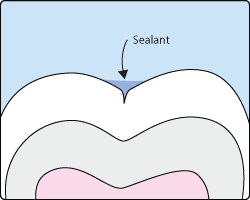
Sometimes brushing is not enough, especially when it comes to those hard-to-reach spots in your child’s mouth. It is difficult for a toothbrush to reach between the small cracks and grooves on teeth. If left alone, those tiny areas can develop tooth decay. Sealants give your child’s teeth extra protection against decay and help prevent cavities.
Dental sealants are plastic resins that bond and harden in the deep grooves on the tooth’s surface. When a tooth is sealed, the tiny grooves become smooth, and are less likely to harbor plaque. With sealants, brushing becomes easier and more effective against tooth decay.
Sealants are typically applied to children’s teeth after their permanent teeth have erupted as a preventive measure against tooth decay. It is more common to seal “permanent” teeth rather than “baby” teeth, but every patient has unique needs, and the dentist will recommend sealants on a case-by-case basis.
Sealants last from three to five years, although it is fairly common to see adults with sealants still intact from childhood. A dental sealant only provides protection when it is fully intact so if your child’s sealants come off, let the dentist know, and schedule an appointment for your child’s teeth to be re-sealed.